Shrimp flavin is found in river crayfish shell, oysters and salmon, which is a sort of red carotenoid, It can be combined with the protein in vivo and show green, blue. There are antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-tumor, prevention of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.
Astaxanthin is a kind of lutein, the most widely distributed in the animal kingdom. It is pink, and has unique coloring function, also can promote antibody production, enhancing animal immunity. On the aspects of the antioxidant and scavenging free radicals, the ability is stronger than β-carotene( (10 times). It is soluble in water and lipophilic, soluble in carbon disulfide, acetone, benzene and chloroform and other organic solvents. Astaxanthin is a kind of very potential carotenoid additives, and has a broad prospect in food, feed, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and other fields. Foods which are rich in the astaxanthin include marine plants, Pluvialis microalgae, Phaffia rhodozyma, wild salmon, shrimp, salmon, rainbow trout and other seafood. Astaxanthin can bring many benefits to health, but not everyone can get enough, this is where the problem.
Natural astaxanthin also known as astacin, is a kind of precious health ingredients, is used for development to enhance immunity, anti-oxidation, anti-inflammatory, eyes and brain health, regulating blood lipids and other natural and healthy products. At present, the main used as a raw material for human health food and medicine; aquaculture (currently the main salmon, trout and salmon), poultry feed additive and additives of cosmetics.
It can significantly improve the body's immunity, because of its non-specific combination with skeletal muscle, can effectively remove the free radicals which are generated by the movement of the muscle cells, strengthen aerobic metabolism, so it has a significant anti fatigue effect.
It is only the carotenoids through blood brain barrier, with true anti-aging effect and effective antioxidant is the basis of all beauty activities. Owing to its powerful antioxidant, It can effectively wrinkle anti-aging, sunscreen whitening and except for chloasma caused by age. In the prevention and treatment for age related macular degeneration and improvement of retinal function, it has good effects. All of the above can clearly be confirmed in the United States.
The stability and antioxidant activity of synthetic astaxanthin also are lower than natural astaxanthin. Because of the hydroxyl (-OH) at ends of the molecule, astaxanthin can be esterification, resulting in not the same of its stability. More than 90% of natural astaxanthin is exist in ester form, and therefore more stable. Synthesic astaxanthin is the free state, therefore, the stability is not the same, must be embedded in order to stabilize. Because Left lateral structure of synthesic astaxanthin was only about 1/4, so it is only natural antioxidant of 1/4.
A method of production of chitin, astaxanthin, protein, calcium powder and biological fertilizer from shrimp shell, its production process is as follows:
1. The shrimp shell is cleaned and mechanical crushing to 5-10 mesh t.
2. The weight ratio of the shrimp shell powder and the shrimp shell was 1: 1-2, and the protease was added to the solution. According to different varieties of shrimp shell, the temperature of the enzyme solution was 30-70℃, pH value was 4-8, the time was 2-6 hours, and protease was 0.4%-1% of the shrimp shell in weight .
3. After the end of the enzyme solution, the temperature is up to 70-100℃ and then Enzyme bacteria is cool.
4. After that, adding organic solvent extraction, the weight ratio of organic solvent and shrimp shell was 1: 1-2, stirred closed fully 6-12 hours then cooling.
5. After full reaction, separate the liquid of shrimp and shrimp.
6. Shrimp liquid is divided into liquid and organic liquid.
Natural astaxanthin also known as astacin, is a kind of precious health ingredients, is used for development to enhance immunity, anti-oxidation, anti-inflammatory, eyes and brain health, regulating blood lipids and other natural and healthy products. At present, the main used as a raw material for human health food and medicine; aquaculture (currently the main salmon, trout and salmon), poultry feed additive and additives of cosmetics. It can significantly improve the body's immunity, because of its non-specific combination with skeletal muscle, can effectively remove the free radicals which are generated by the movement of the muscle cells, strengthen aerobic metabolism, so it has a significant anti fatigue effect.
Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
(1) Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant. The free radical scavenging activity of astaxanthin protects lipids from peroxidation and reduces oxidative damage of LDL-cholesterol (thereby reducing arterial plaque formation), cells, cell membranes, mitochondrial membranes. Astaxanthin increases strength and endurance.
(2) Astaxanthin seems to improve the immune system by increasing the number of antibody producing cells. Astaxanthin enhances antibody production by exerting actions on T-cells and T-helper cells. Astaxanthin is used to treat neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
(3) Astaxanthin protects the eyes and skin from sun radiation damage by quenching singlet and triplet oxygen. Studies with rats show that astaxanthin reduces retinal injury.
(4) Studies have shown the anti-cancer effects of astaxanthin in rodents. The inhibitory effect of astaxanthin on cancer is stronger han that of beta-carotene.
Side Effects of Astaxanthin
You should also know about the side effects of astaxanthin. No toxic side-effects are related with overdose of astaxanthin. However, mild to moderate side effects are noticed with high doses of it. Some side effects include:
- Aplastic anemia
- Eye damage because of crystal formation
- Decreased libido
- Reduction in blood pressure,
- Enhanced skin pigmentation
- Gynecomastia (abnormal enlargement of breasts in men)
- Inhibited 5-alpha-reductase
- Increased hair growth
- Lowered eosinophil counts
- Parathyroid intervention
- Lowered serum calcium
- Inhibited conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
Research has shown that the optimal dosage of astaxanthin is 4 mg per day-which relates to 200 mg of a 2% extract.
It is of prime importance that when evaluating any Astaxanthin supplement that you ensure that you ingest 4 mg PER DAY-which would require 200 mg of a 2% extract-as used in our Anti-Aging Supplement.
Toxicity and symptoms of high intake Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is practically non-toxic in acute animal studies at doses up to 18 grams. When tested for genotoxicity, there was no evidence for mutagenicity in Ames/Salmonella assays nor did it induce micronuclei when tested in vivo up to 2000 mg/kg in mice. There was no maternal, embryo-toxic or teratogenic effects in a teratology study in rabbits given up to 400 mg/kg over most of the gestational period.
No adverse effects were noted in a one-generation reproduction study at doses up to 400 mg/kg in rats. In multiple subchronic feeding studies in rats, astaxanthin did not produce any adverse toxicological effects.
Carotenoid pigment found mostly in animal organisms, but also occuring in plants; thought to be the precursor of astacin. Animal studies indicate that it reduces blood glucose and ameliorates several
parameters of the diabetic metabolic syndrome. It improves blood flow and vascular tone in models of hypertension.
astaxanthin is an anti-oxidant. Molecularly, astaxanthin is similar to beta-carotene, but in clinical studies it appears to demonstrate stronger anti-oxidant properties, including an ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation and an anti-inflammatory capacity. It is used in cosmetics for its anti-oxidant properties, and for possible uV protection abilities. Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring pigment, part of the carotenoid group, and found in many foods. It is what provides salmon and certain crustaceans (e.g., shrimp, crab, lobster) with their reddish tint. Astaxanthin can also be synthetically produced.
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found primarily in marine animals including shrimp and salmon. It is a potent lipid-soluble antioxidant.
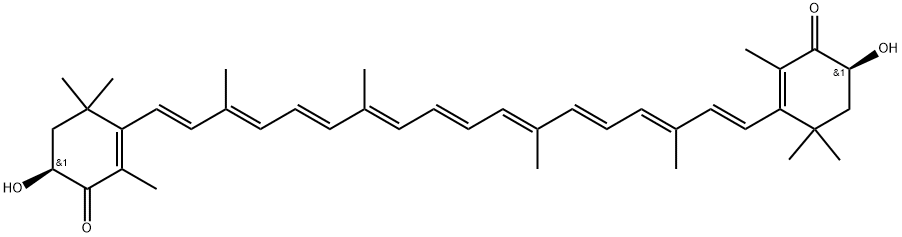
ChEBI: Astaxanthin is a carotenone that consists of beta,beta-carotene-4,4'-dione bearing two hydroxy substituents at positions 3 and 3' (the 3S,3'S diastereomer). A carotenoid pigment found mainly in animals (crustaceans, echinoderms) but also occurring in plants. It can occur free (as a red pigment), as an ester, or as a blue, brown or green chromoprotein. It has a role as an anticoagulant, an antioxidant, a food colouring, a plant metabolite and an animal metabolite. It is a carotenone and a carotenol. It derives from a hydride of a beta-carotene.
Biotechnological Production
Commercial production processes are known in which astaxanthin production is
performed in closed photobioreactors by Cyanotech Corporation (Hawaii).
This mode of cultivation strongly improves process control, algae predation, and
production, but the fermentation costs are significantly higher. These higher
costs have to be compensated by high productivity levels and more efficient
downstream processing in order to make a competitive product.
Most of the astaxanthin available on the world market has been produced
chemically since the 1950s, for example, by DSM and BASF, and the process is
efficient and cost-effective. There are also microbial sources, for example,
X. dendrorhous (previously described as P. rhodozyma), and the alga H. pluvialis.
X. dendrorhous has been widely investigated as to its potential of astaxanthin
production for salmonids. This has resulted in a race between companies
in the 1980s and 1990s. Natural astaxanthin is currently available as a
spray-dried powder (5–10 mg astaxanthin/g), and is supplemented to fish feed to
give salmonid flesh its pink color. Another astaxanthin application is in the
nutraceutical market, as astaxanthin is regarded as a potential antioxidant.
With regard to production by algae, H. pluvialis is the only species commercially
cultivated for astaxanthin production. This green alga is able to grow under
autotrophic, heterotrophic, and mixotrophic conditions. An example of the latter is
its ability to grow in the presence of acetate and light. Astaxanthin accumulates
in response to stress in lipid globules of the cells.
all-trans-Astaxanthin is a ketocarotenoid, most commonly identified in marine and aquatic animals, including krill, wild salmon, rainbow trout, microalgae, shells of lobster, shrimp, seafood products, etc. It is biologically known as a vitamin A precursor, and exhibits strong antioxidant property, much higher compared to vitamin E and β-carotene. Its role in food and the medicinal industry is also well-defined.
Astaxanthin is a potent carotenoid antioxidant found in marine algae, red yeast and many other plant and animal sources. Animal studies indicate that it reduces blood glucose and ameliorates several parameters of the diabetic metabolic syndrome. It improves blood flow and vascular tone in models of hypertension. In vitro studies indicate that it upregulates connexin 43 and thus, may be chemopreventive against cancer.