3,3'-Diaminobenzidine: properties, applications and toxicity
General Description
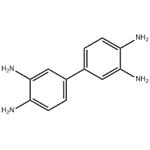
3,3'-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) is a white solid with the formula C12H14N4. It is soluble in water and has various applications. It serves as a coupling reagent in immunohistochemistry, producing a brown precipitate to detect proteins. DAB is also used in dye synthesis, polyurethane production, and other polymer applications. However, its use in immunohistochemistry can lead to false-positive results and background staining. DAB is potentially toxic, causing skin and organ damage in animals. In humans, inhalation exposure can result in respiratory irritation, while high doses can lead to gastrointestinal issues and hypotension. Occupational exposure may increase the risk of certain cancers. Further research is needed to fully understand its carcinogenic potential in humans.

Figure 1. 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine
Properties
3,3'-Diaminobenzidine is a white solid that is soluble in water and has the formula C12H14N4. It is used as a coupling reagent in immunohistochemistry to detect the presence of certain proteins by forming a brown-colored precipitate in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. It is also used in the manufacture of certain dyes and in the production of polyurethane and other polymers. 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine is considered a precusor to the synthesis of melanin, and it has been shown to produce both soluble and insoluble melanin-like pigments from oxidation with hydrogen peroxide. These pigments can be formed at pH 4-7 and are thought to be responsible for the coloration of hair, eyes, and skin. The use of 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine as a peroxidase substrate in immunohistochemistry has been associated with an increased risk of false-positive results and background staining. This is thought to be due to the autoxidation of the diamine in the presence of peroxidase, leading to the formation of reactive oxygen species that can nonspecifically bind to proteins. To reduce these issues, certain controls and techniques have been developed, such as using a peroxidase block or a peroxidase inhibitor during the staining process. 1
Applications
3,3'-Diaminobenzidine has a wide range of applications in both academic and industrial settings. One of its most common uses is in immunohistochemistry, where it is used as a coupling reagent to detect the presence of certain proteins. By forming a brown-colored precipitate in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine provides a visual signal that can be easily detected under a microscope. This reaction is commonly used to study the localization and expression of enzymes, receptors, and other cellular components. In addition to its use in immunohistochemistry, 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine is also employed in the synthesis of certain dyes. It serves as a precursor in the production of various azo dyes, which are commonly used in textile manufacturing and other industries. Furthermore, 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine finds utility in the production of polyurethane and other polymers. By reacting with various diisocyanates, it can be used to create cross-linked polymers that exhibit good mechanical strength and resistance to heat and chemicals. These polymers have applications in adhesives, coatings, and sealants, among others. Overall, 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine serves as a versatile intermediate in various chemical reactions and finds applications in dye synthesis, polymer production, and immunohistochemistry. Its ability to undergo oxidation and coupling reactions makes it a valuable reagent in these fields. 2
Toxicity
3,3'-Diaminobenzidine is a substance that has been associated with potential toxic effects in both animals and humans. The toxicity of DAB primarily results from its oxidation and subsequent reaction with proteins or other molecules. In animals, oral or dermal exposure to high doses of DAB has been reported to cause adverse effects such as irritation, hypersensitivity reactions, and damage to the liver, kidneys, and skin. Studies in rodents have also shown that DAB can induce DNA damage, which may increase the risk of developing tumors. However, the carcinogenic potential of DAB in humans remains controversial and requires further investigation. In humans, inhalation exposure to DAB has been associated with respiratory tract irritation, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Exposure to high doses of DAB has also been reported to result in nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hypotension. Additionally, occupational exposure to DAB has been linked to an increased risk of developing certain types of cancers, such as bladder cancer. 3
Reference
1. Litwin JA. Histochemistry and cytochemistry of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine. A review. Folia Histochem Cytochem (Krakow), 1979, 17(1):3-28.
2. Gupta B, Yang G, Petrauskene O, Key M. Recent Advances in Chromogens for Immunohistochemistry. Methods Mol Biol, 2023, 2593:35-50.
3. Topics: medicine-and-dentistry diaminobenzidine. Sciencedirect, 2013. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/diaminobenzidine
);You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine manufacturers

US $0.00/kg2024-04-12
- CAS:
- 91-95-2
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 2000ton
US $0.00-0.00/kg2024-01-02
- CAS:
- 91-95-2
- Min. Order:
- 0.1kg
- Purity:
- 0.98
- Supply Ability:
- 500kg




