How to synthesize Tenapanor hydrochloride?
Overview
Tenapanor hydrochloride, also known as AZD-1722 and RDX5791, is a selective sodium hydrogen exchanger 3 (NHE3) inhibitor developed by Ardelyx and approved by the USFDA for the treatment of constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C). This drug is also used for the treatment of hyperphosphataemia in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis or with end-stage renal disease (ESRD)[1].
Inhibition of NHE3 on enterocytes in the gut epithelium reduces the absorption of sodium ions and increases water secretion, accelerating gut transit time. The recommended dose of tenapanor hydrochloride is 50 mg, administered orally twice daily. The high molecular weight and two primary amines within the lengthy dimeric structure of tenapanor likely contribute to its absorption profile, rendering it a gut-restricted GI-targeted drug.
Synthesis method
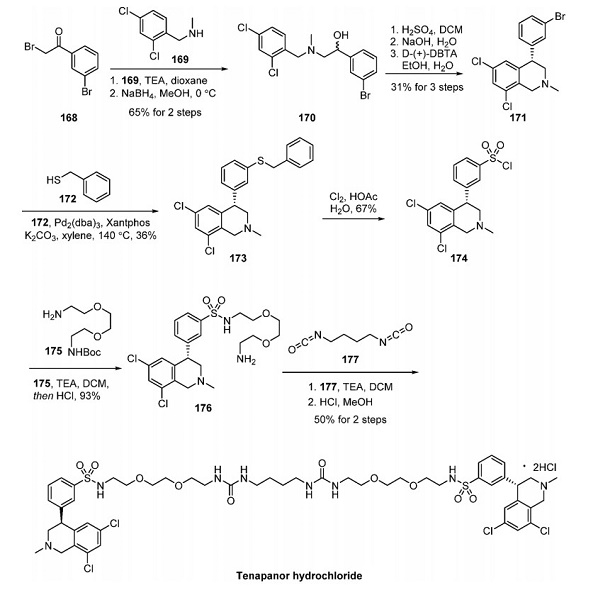
A multigram synthesis and details of the isolation of the API and its crystalline forms were described by Teva Pharmaceuticals, and this approach is shown in the above figure[2]. Bromoacetophenone 168 was reacted with amine 169, and the resulting ketone was reduced with sodium borohydride to furnish racemic alcohol 170 in 65% yield over two steps. Compound 170 then underwent an intramolecular cyclization under acidic conditions, and the resulting tetrahydroisoquinoline was resolved using D-dibenzoyl tartaric acid (D-(+)-DBTA) to afford enantiomerically pure az cycle 171 in 31% yield over three steps.
Buchwald−Hartwig introduction of benzenethiol gave rise to mercaptan 173, albeit in modest yield. Gaseous chlorination in the presence of acetic acid converted the benzyl thioether to sulfonyl chloride 174, setting the stage for the dimerization sequence. Teva’s approach employed the reaction of sulfonyl chloride 174 with diamine 175 under mildly primary conditions, followed by Boc deprotection to prepare amine 176. This compound was then reacted with bis(isocyanate) 177 and base followed by methanolic HCl. The protocol produced tenapanor as the bis(hydrochloride) salt in 50% yield.
References
[1] Markham, A. “Tenapanor: First Approval.” Drugs 79 1 (2019): 1897–1903.
[2] Andrew C. Flick. “Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved during 2019.” Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 64 7 (2021): 3604–3657.
);