Rhodamine B: Applications, toxicity and metabolism
General description
Rhodamine B is a basic red dye and extremely water-soluble of the xanthene class. Rhodamine B possesses 479.02 g/mol as molecular weight and wavelength absorbance (A) at 554 nm (λ max). Rhodamine B dyes family was among the oldest and most widely used synthetic dyes and was used in various industrial areas. Rhodamine B is among the most environmentally friendly xanthene class’s basic dyes. Rhodamine B is a cationic dye with a high water-solubility, commonly utilised as medicine (for animals), in the staining of biological trials, printing, and textile industry. Rhodamine B is known to have harmful and cancerous, respiratory diseases and kidney failure. Rhodamine B cause eye irritation towards humans as this product contains a cationic dye. Rhodamine B poses a threat to aquatic life by obstructing light penetration, resulting in decreased photosynthesis. The numbers of zooplankton and phytoplankton are less in Rhodamine B -polluted water. Rhodamine B is originally used to colour fabrics, and acts as water tracing agents, fluorescent markers for microscopic structure tests, photosensitisers and laser dyes because of their special optical properties. The poisonous effects of Rhodamine B on humans and creatures have been recorded and causing hypersensitive dermatitis, changes, skin disturbances, and disease [1]. Its appearance is as follows:
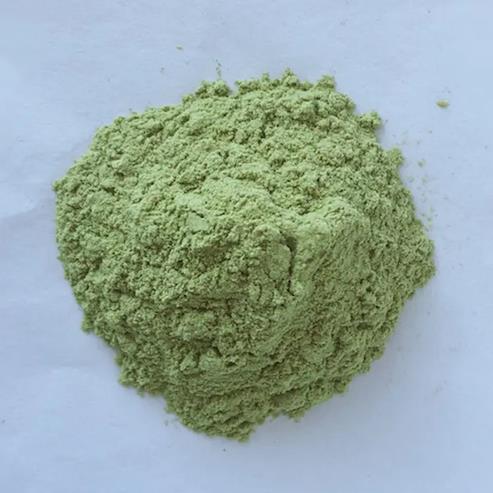

Figure 1 Appearance of Rhodamine B
Applications
Aside from its major applications, Rhodamine B is often used as a tracer dye, e.g. to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport of water. Rhodamine B fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine B is used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Rhodamine B is also used in biochemistry to inhibit mitochondrion function. It seems to bind to the mitochondrion membranes and inhibit transport processes, especially the electron transport chain, thus slowing down inner respiration. It is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (Pgp), which is usually overexpressed in cancer cells. Recent reports indicate that rhodamine B may be also a substrate of multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP), or more specifically, MRP1.
Toxicity
A total of 28 female rats were divided into four groups consisting of control; groups treated with rhodamine B at doses of 4.5; 9, and 18 milligram/200 gram body weight. Rhodamine B was administered orally for 36 days with the probe. Analysis of MDA level was done spectrophotometrically. Analysis of the number of ovarian follicles and thickness of endometrium was done histopathologically by hematoxylin eosin staining. Analysis of 17β- estradiol level was done by ELISA. Rhodamine B administered in different doses in female rats can increase ovarian MDA levels significantly than the control (P < 0.05). Administration of rhodamine B of the second and third doses in female rats can reduce the number of primary, secondary, and De Graaf follicles significantly compared to the control (P < 0.05). Administration of rhodamine B of the second and third doses in female rats can reduce 17β-estradiol level significantly compared to the control (P < 0.05). The administration of rhodamine B could reduce thickness of endometrium significantly compared to the control (P < 0.05). It was concluded that administration of rhodamine B triggered ovarian toxicity through oxidative stress, a decrease in the number of follicles, and decreased level of 17β-estradiol which ultimately lowered the thickness of endometrium [2].
Metabolism
Rhodamine B was de-ethylated when ingested by animals. Two of three observed metabolites were identified as 3′,6′-diaminofluoran, and N,N′-diethyl-3′,6′-diaminofluoran on the basis of their Rf values, fluorescence, color, diazotization characteristics, and activation and fluorescence spectra when compared to synthetic counterparts. Evidence presented indicates that the third metabolite is the monoethylated analog of Rhodamine B. Feeding studies with synthetic counterparts of the identified metabolites indicated that the basic fluoran structure of the Rhodamine B molecule was not destroyed and strengthened other evidence that no chemical changes other than de-ethylation occurred during the metabolism [3].
References
[1]Al-Gheethi A A, Azhar Q M, Kumar P S, et al. Sustainable approaches for removing Rhodamine B dye using agricultural waste adsorbents: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 132080.
[2]Sharma J, Sharma S, Bhatt U, et al. Toxic effects of Rhodamine B on antioxidant system and photosynthesis of Hydrilla verticillata[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials Letters, 2022, 3: 100069.
[3]Webb J M, Hansen W H. Studies of the metabolism of rhodamine B[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 1961, 3(1): 86-95.
);You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Rhodamine B manufacturers

US $6.00/KG2024-04-23
- CAS:
- 81-88-9
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- More than 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 2000KG/Month

US $8.00/kg2024-01-04
- CAS:
- 81-88-9
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 2000