Synthesis and Application of Oseltamivir acid
General description
Oseltamivir, an antiviral drug used for the treatment of influenza, contains the L-glutamic acid motif in its chemical structure. We focused on this structural characteristic of oseltamivir and examined the pharmacologic effects of the drug on the nervous system in invertebrate and vertebrate animal models. Injection of oseltamivir or L-glutamic acid into silkworm (Bombyx mori) larvae induced muscle relaxation. Oseltamivir and L-glutamic acid inhibited kainate-induced rapid muscle contraction, but neither drug affected insect cytokine paralytic peptide-induced slow muscle contraction. In the mammalian system, mice (Mus musculus) treated intracerebrally with oseltamivir developed convulsive seizures. Hydrolyzed oseltamivir, the active form containing a carboxylic acid, evoked epileptiform firing of hippocampal neurons in rat (Rattus norvegicus) organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. These results are the first to demonstrate that oseltamivir exerts pharmacologic effects on the nervous system in insects and mammals.
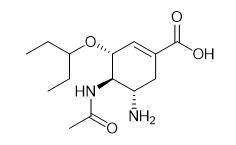
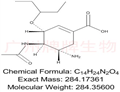
Fig. 1 The structure of Oseltamivir acid.
Synthetic routes
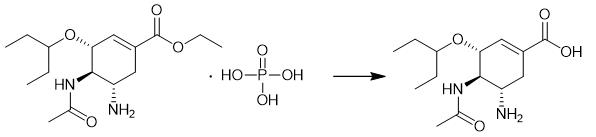
Fig. 2 The synthetic method 1 of Oseltamivir acid.
Add a 25% NaOH solution (10 mL) to oseltamivir-H3PO4 (820 mg, 2 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane/H2O (28 mL/4 mL). Stir the reaction mixture at room temperature. When the starting material is completed, neutralize the reaction mixture with concentrated and 1N aqueous HCl solutions to reach a pH between 4.2-4.3. Dissolve the mixed solution in AcOEt (3 × 50 mL) and H2O (15 mL). Dry the organic phase with MgSO4. Filter the organic phase. Evaporate the organic phase to dryness [1].

Fig. 3 The synthetic step 1 of method 2 of Oseltamivir acid.
Add chlorotrimethylsilane (167 mg, 1.54 mmol, 0.19 mL) into a flask with zinc powder (1.30 g, 20 mmol) and dry ether (35 mL). Stir the mixture for 15 min at room temperature under an inert atmosphere. Filter activated zinc under an inert atmosphere (Ar), wash with dry ether (2 × 10 mL). Add ethyl- (3R, 4R, 5S) -4-acetamido-5-nitro-3- (pentane-3-yloxy) cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate (263 mg, 0.77 mmol) and acetic acid (15.6 mg, 260 mmol, 14.9 mL) into the flask with activated zinc. Stir the mixture under reflux for 8 h. Filter off zinc and wash with EtOAc. Concentrate the filtrate under reduced pressure. Purify the product by column chromatography (SiO2, EtOAc/MeOH 2 : 1). Scale gram 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ6.79 (t,J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 5.53 (br d,J= 7.6 Hz, 1H), 4.29.-.4.12 (m, 3H), 3.52 (dt, J = 10.3, 8.3 Hz, 1H), 3.35 (dd,J = 11.4, 5.7 Hz, 1H), 3.25 (ddd.J= 15.4, 10.1, 5.0 Hz, 1H), 2.75 (dd,J= 17.7, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 2.25.-.2.08 (m, 1H), 2.04 (s, 3H), 1.76 (br s, 2H), 1.62.-.1.41 (m, 4H), 1.34.-.1.23 (m, 3H), 0.90 (td,J = 7.4, 2.4 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ171.1, 166.5, 137.7, 129.6, 81.8, 74.9, 61.0, 59.1, 26.4, 25.8, 23.8, 14.3, 9.7, 9.5. IR 3281s (N.-.H), 2922m (C.-.H), 1710s (C=O), 1630s (C=C), 1544 (N.-.H) [2].

Fig. 4 The synthetic step 2 of method 2 of Oseltamivir acid.
Add 1 M water solution of NaOH (27.5 mg, 0.69 mmol) into a flask with aminoester (3R, 4R, 5S) -1 (135 mg, 0.43 mmol) dissolved in THF (14.2 mL) at 0 °C. Stir the reaction mixture at 65 °C for 1 h. Keep TLC detection by adding acidic amberlite (2 g). Stir the mixture for next 15 min and filter off amberlite. Wash with EtOH. Evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure and purify the product by flash chromatography (reverse column, acetonitrile/H2O 19:1). Scale milligram 1H NMR (300 MHz, D2O): δ6.53.-.6.50 (m, 1H), 4.30 (d,J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 4.06 (dd,J = 11.6, 8.9 Hz, 1H), 3.60.-.3.51 (m, 2H), 2.90 (dd,J = 17.1, 5.5 Hz, 1H), 2.56.-.2.43 (m, 1H), 2.10 (s, 3H), 1.68.-.1.36 (m, 4H), 0.89 (dt,J = 14.4, 7.4 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (75 MHz, D2O): δ175.1, 173.7, 132.9, 132.5, 84.2, 75.6, 52.9, 49.7, 29.4, 25.4, 25.1, 22.3, 8.5, 8.4 [2].
Application
Increases dopamine levels
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu (R)), a neuraminidase inhibitor, is effective for treating both seasonal flu and H5N1 influenza A virus infection. Oseltamivir is generally well tolerated, and its most common adverse effects are nausea and vomiting. However, neuropsychiatric behaviors including jumping and failing from balconies by young patients being treated by oseltamivir have been reported from Japan; this has led to warnings against its prescribing by many authorities. The pharmacological mechanism of the neuropsychiatric effects of oseltamivir remains unclear. Many studies reported that changes in neurotransmission and abnormal behaviors are closely related. We investigated the changes in dopamine and serotonin metabolism after systemic administration of oseltamivir in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of rats by using microdialysis. After systemic administration of oseltamivir (25 mg/kg or 100 mg/kg; intraperitoneally (i.p.)), extracellular dopamine in the mPFC was significantly increased as compared to the control values; 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid, the metabolites of dopamine, had also increased significantly. Serotonin was unchanged after the administration of oseltamivir. These findings suggest that oseltamivir increased dopamine release in the mPFC; further, they suggest that the increase in dopamine during oseltamivir treatment may have caused abnormal behaviors in young patients. in cases where oseltamivir is prescribed to children, close observation is required [3].
Defense Against Swine Flu
Oseltamivir (has known by its brand name 'Tamiflu') is a prodrug, requiring ester hydrolysis for conversion to the active form, Oseltamivir carboxylate. Oseltamivir was the first orally active neuraminidase inhibitor commercially developed by US based Gilead Sciences and is currently marketed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche (Roche). Oseltamivir is an antiviral drug which works by blocking the function of the viral neuraminidase protein. US FDA approved Oseltamivir for prophylaxis of uncomplicated influenza A and B. Currently, Oseltamivir is the only first line defense drug available for the treatment of Swine Flu. Orally Oseltamivir is well tolerated and effective in treatment of influenza in adolescents and adults, including the elderly and patients with chronic cardiac and/or respiratory disease. Many of the pharmaceutical companies targeted Oseltamivir as a block buster molecule. In present review, we have tried to cover chemistry, mode of binding, total synthesis, current patent status, adverse effect and clinical status of Oseltamivir giving emphasis on medicinal chemistry aspect [4].
Induces favorable response on oxidative damage
The purpose was to measure the effect of Oseltamivir on oxidative biomarkers and dopaminergic and serotonergic systems in brain of rats with induced hypotriglyceridemia by Bezafibrate. Male young Wistar rats were treated as follows: group 1, NaCl 0.9%, (Controls); group 2, Oseltamivir (100 mg/kg); group 3, single dose of Bezafibrate (150 mg/kg); group 4, four dose of Bezafibrate; group 5, si);
You may like
See also
Lastest Price from OSELTAMIVIR ACID manufacturers
US $0.00-0.00/mg2024-04-10
- CAS:
- 187227-45-8
- Min. Order:
- 10mg
- Purity:
- 90%+
- Supply Ability:
- 10g

US $0.00/mg2022-04-21
- CAS:
- 187227-45-8
- Min. Order:
- 10mg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10KG