The Chemical property of Phosphine
Description
Phosphine, or Phosphorous trihydride, is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula PH3, classed as a pnictogen hydride. It is one of the most commonly used fumigants globally for the disinfestation of cereal grains, legumes, seeds, dried fruit, tree nuts, other durable food commodities, and many processed foods[1]. It has the unusual property that it can be generated from solid formulations of metallic salts of aluminum phosphide and magnesium phosphide[2].
Chemical property
Its pure form is odorless, and other forms have an unpleasant odor, like rotten fish or garlic, due to the presence of substituted Phosphine and Diphosphate. PH3 has a similar structure to NH3 (ammonia), which makes sense since phosphorus and nitrogen are in the same group (pnictogens). Phosphine has a central phosphorous (P) atom. It is bonded to three hydrogen (H) atoms through single covalent bonds. Phosphorous has a lone electron pair that repels the bonding pairs. As a result, the PH3 molecule becomes asymmetric, resulting in a bent structure. The molecular geometry of PH3 has a deviation from the trigonal pyramidal structure, with a bond angle of 93.5°.
Polarity Molecule
PH3 is polar due to a lone pair of electrons with electron-electron repulsion, causing an overall "bent" structure. This results in a dipole moment throughout the molecule. Thus, PH3 is overall polar (net µ = 0.58 Debye).
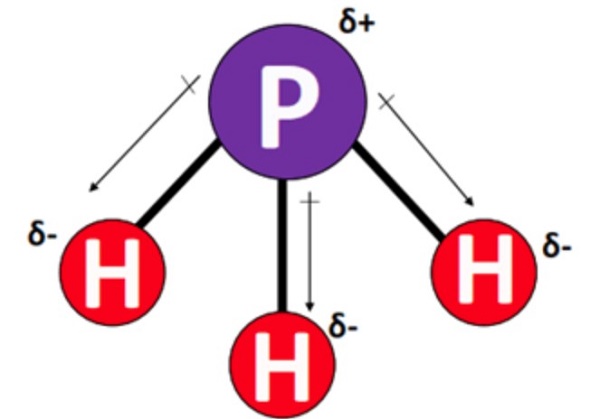
However, the bonds within the molecule are considered non-polar covalent. This is due to a minimal electronegativity difference of 0.01 units between the bonded phosphorus atoms and hydrogen in each P-H bond in the PH3 molecule. Thus, each P-H bond is very weakly polar or almost non-polar in PH3 and possesses a very small dipole moment value (symbol µ).
References
[1] Yong Huang. “Susceptibility of Tribolium castaneum to phosphine in China and functions of cytochrome P450s in phosphine resistance.” Journal of Pest Science 31 1 (2019): 1239–1248.
[2] E.M. Thoms. “Fumigants.”Encyclopedia of Food and Health (2016): 150-156.
);