The synthesis and application of acetamide
Background
Acetamide is an organic compound with molecular formula C2H5NO[1], molecular weight 59.07, density 1.159, melting point 79-81 ° C, boiling point 221 ° C and water solubility 2000g / L (20 ° C). Acetamide is mainly used as organic solvent, plasticizer and stabilizer of peroxide. It is also used as antacid in cosmetics production and in the preparation of sleeping pills and pesticides. The appearance and properties of pure acetamide are colorless, transparent and acicular crystals. Acetamide is colorless, transparent, needle like crystal with the smell of rat secretion. It is easy to deliquesce, flammable and low toxic. Melting point 81 ℃, boiling point 221 ℃ (100KPA), 120 ℃ (2.66kpa), relative density 1.159 (20 / 4 ℃), refractive index 1.4274. Acetylamine is soluble in water, ethanol, chloroform, pyridine and glycerol, and slightly soluble in ether.
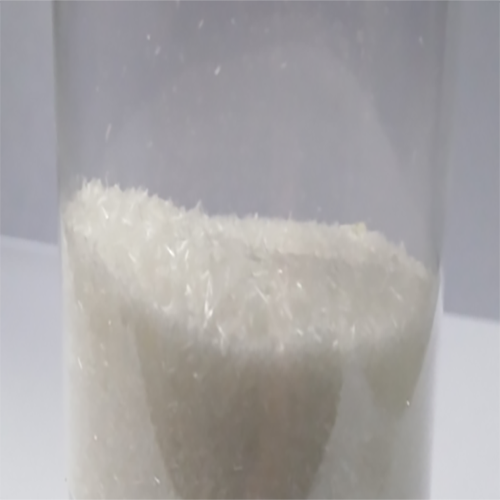

Picture 1 Acetamide powders
Chemical properties of acetamide
When the acetamide aqueous solution is heated, it is hydrolyzed to produce ammonium acetate. Acetonitrile is formed when heated with a strong dehydrating agent such as phosphorus pentoxide[2]. It reacts with methylamine hydrochloride to produce N-methylacetamide ch3conhch3. In acetic acid solution, n-acetylacrylamide is formed by reacting with acetylene and carbonyl nickel at 40 ~ 50 ℃. React with nitrous acid to generate acetic acid and nitrogen; react with sodium hypochlorite in alkaline solution to form n-chloroacetamide, and then Hofmann reaction to generate methylamine; react with Trichloroacetaldehyde to generate ccl3ch (OH) nhcoch3. When acetamide aqueous solution is irradiated by sunlight in the presence of calcium carbonate, photolysis reaction occurs. This product is highly toxic. It can be absorbed through the skin and strongly irritates the eyes, skin and mucous membrane. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 20 * 10-6. Its toxicity is stronger than dimethylformamide. Protective equipment must be worn for on-site operation. After splashing the skin, rinse with plenty of water.
Synthesis of acetamide
Laboratory synthesis can be carried out according to the following steps. Put 3kg glacial acetic acid into a 5L flask and add ammonium carbonate equivalent to 400g ammonia. The flask is equipped with a high-efficiency fractionation column, a condenser and a receiver. Heat the reaction mixture until it boils slowly, adjust the heating so that the distillation rate does not exceed 180mg / h until the top temperature reaches 110 ℃. A mixture of 1400-1500 ml of water and acetic acid was obtained. Change the receiver, slowly increase the heating, and continue the distillation at the same speed until the top temperature rises to 140 ℃. The distillate is 500-700ml, mainly acetic acid, which is reserved for the next feeding. Transfer the residue into a flask with fractionation column and air condenser, distill under normal pressure, and collect the fractions before 210 ℃ and 210-216 ℃ respectively. The latter is acetamide, weighing 1150-1200g. The former can also distill and recover some products. The total weight of the two is 1200-1250g, and the yield is 87% - 90%.
The recrystallization of acetylamine is usually carried out by distillation and solvent recrystallization. The commonly used solvents are acetone, benzene, ethyl acetate, methyl acetate, chloroform, dioxane or the mixture of benzene and ethyl acetate. For example, 1kg of acetamide prepared by the above method is recrystallized with a mixed solvent of 1l benzene and 300ml ethyl acetate to obtain a colorless needle like pure product. The purity of products obtained from industrial production shall not be lower than 98%, and the freezing point shall not be lower than 76 ℃.
Application of acetamide
Acetamide has high dielectric constant and is an excellent solvent for many organic and inorganic substances. It is widely used in various industries. It can be used as solubilizer when some substances with low water solubility are dissolved in water, such as solvent and solubilizer for dyes in fiber industry and solvent in the synthesis of antibiotics such as chloramphenicol. Acetamide has weak alkalinity and can be used as an antacid for varnish, explosives and cosmetics. Acetamide is hygroscopic and can be used as a wetting agent for dyeing; It can also be used as plasticizer of plastics. N-haloacetamide produced by chlorination or bromination of acetamide is a halogenated reagent of organic synthesis. Acetamide is also a raw material for the manufacture of drugs and fungicides. Acetamide is an antidote to fluoroacetamide poisoning. The mechanism of action is that the chemical structure of the product is similar to that of Fluoroacetamide, which can compete for acetylaminase, so that fluoroacetamide does not produce fluoracetic acid, and eliminate the toxic effect of the latter on the tricarboxylic acid cycle to achieve the purpose of detoxification.
Reference
1 He liangnian, Li Kai, Liu Xiaopeng, etc α- Study on structure-activity relationship of herbicidal activity of aromatic aminoacetamide. Chemistry and Bioengineering, 1998
2 Liu Lixin, Han dewu, Ren Dabin Role of enterogenous endotoxemia in the pathogenesis of liver injury induced by thioacetamide. Chinese Journal of liver diseases, 2000
);You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Acetamide manufacturers

US $100.00/kg2024-04-24
- CAS:
- 60-35-5
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99
- Supply Ability:
- 5000
US $1.10/g2024-04-17
- CAS:
- 60-35-5
- Min. Order:
- 1g
- Purity:
- 99.0% min
- Supply Ability:
- 100 tons min