Uses and Preparation of Pregabalin
General description
Pregabalin is a 3-isobutyl derivative of gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) with anti-convulsant, anti-epileptic, anxiolytic, and analgesic activities [1]. CAS number is 148553-50-8. Pregabalin is also known as (S)-3-(Aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid CI-1008 PD-144723; PREDNISOLONESODIUMPHOSPHATE; Pregabalin; Pregablin; Lyrica. This chemical’s molecular formula is C8H17NO2 and molecular weight is 159.22 (Figure 1). Pregabalin is an inhibitor of neuronal activity used for therapy of painful neuropathy and as an anticonvulsant, which selectively binds to alpha2delta (A2D) subunits of presynaptic voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) located in the central nervous system (CNS) to prevent calcium influx and the subsequent calcium-dependent release of various neurotransmitters. It does not bind directly to GABA-A or GABA-B receptors and does not alter GABA uptake or degradation[2].
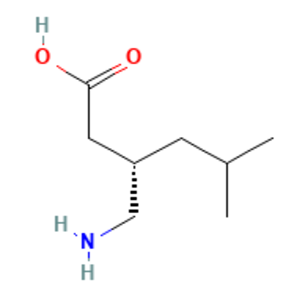
Figure 1 the molecular formula of Pregabalin
Pharmacodynamics
Pregabalin is a beta-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog, and its structure and effect are similar to gabapentin, and it has antiepileptic, analgesic and anxiolytic activities.The mechanism of the antiepileptic action of pregabalin is still unclear.In laboratory studies, pregabalin showed anticonvulsant activity in various epilepsy models; the activity spectrum of animal models was similar to that of gabapentin, but it was 3 to 10 times that of gabapentin. Although the structure of pregabalin is similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it binds the alpha2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. Pregabalin does not modulate dopamine receptors, serotonin receptors, opiate receptors, sodium channels or cyclooxygenase activity[3].
After oral dosing administered in the fasted state, pregabalin absorption is rapid, and extensive, it was used for acute toothache within 30min for approximately 5 h and for 1 week for diabetic neuropathy. Cmax is attained within 1.5 hours after single or multiple doses, and steady state is attained within 24-48 hours with repeated administration. Both Cmax and AUC appear to be dose proportional. The peak reaching time was about 1.5 h, with 90% bioavailability.Less in the liver metabolism, 92% to 99% in the primary form of transrenenal excretion, less than 0.1% of the oral volume with fecal excretion, with a half-life of 5~6.5 h[4].
After oral administration of pregabalin, the reported apparent volume of distribution is roughly 0.5 L/kg. Although pregabalin is not very lipophilic, it is able to cross the blood brain barrier(BBB). System L transporters facilitate the transport of large amino acids across the BBB and it has been confirmed that pregabalin is a substrate. This information suggests that system L transporters are responsible for pregabalin uptake into the BBB. In rat models, pregabalin has been shown to cross the placenta. Pregabalin is eliminated from the systemic circulation primarily by renal excretion as unchanged drug with a mean elimination half-life of 6.3 hours in subjects with normal renal function[5].
Less than 2% of pregabalin is metabolized and it is excreted virtually unchanged in the urine. Following a dose of radiolabeled pregabalin, approximately 90% of the administered dose was recovered in the urine as unchanged pregabalin. The N-methylated derivative of pregabalin, the major metabolite of pregabalin found in urine, accounted for 0.9% of the dose. In preclinical studies, pregabalin (S-enantiomer) did not undergo racemization to the R-enantiomer in mice, rats, rabbits, or monkeys[6].
Mechanism of action
Although the mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, studies involving structurally related drugs suggest that presynaptic binding of pregabalin to voltage-gated calcium channels is key to the antiseizure and antinociceptive effects observed in animal models, that is structurally related to the inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). By binding presynaptically to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, pregabalin modulates the release of several excitatory neurotransmitters. In addition, pregabalin prevents the alpha2-delta subunit from being trafficked from the dorsal root ganglia to the spinal dorsal horn, which may also contribute to the mechanism of action.
Toxicity
The most common adverse effects involve the central nervous system and cognition, including vertigo, dizziness, balance disorder, incoordination, agitation, ataxia, blurred vision, diplopia, amblyopia, somnolence, confusion, restlessness, depression, affective disorder and seizures.
Preparation
Multiple synthetic routes were reported during the initial developmental phases of pregabalin, which can be roughly divided into four categories: (1) preparation of pregabalin by resolution of racemic compounds; (2) Synthesis of pregabalin by desymmetration reaction; (3) Chiral source synthesis; (4) Asymmetric synthesis. Among the above synthetic methods, the latter three have long routes, harsh reaction conditions, high cost and no Conducive to industrial production. However, method (1) has the advantages of simple operation and mild reaction conditions. It is now the main method of industrial production.
Potassium cyanide was used in the first generation pregabalin manufacturing process,however, the high toxicity associated with this compound was a major deterrent in its use.
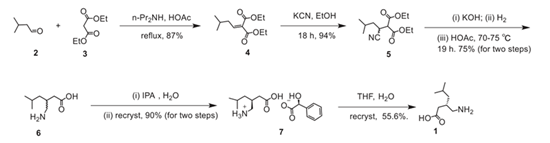
Scheme 1. First-generation pregabalin manufacturing progress
To address this issue and avoid the use of cyanides, Scheme 2 uses rhodium, chiral phosphine, and metal catalysts to yield (S)-pregabalin in high enantiomeric excess.
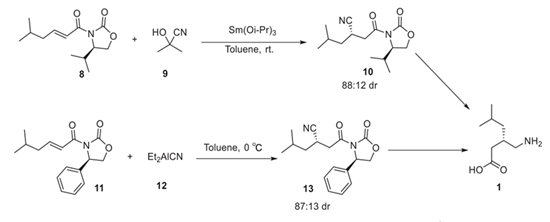
Scheme 2. Michael conjugate addition to the synthesis of (S)-pregabalin.
The asymmetric Michael conjugate addition in the synthesis of (S)-pregabalin involves the reaction of a nucleophile with an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with chiral oxazolidinone substituent. Armstrong et al. reported the synthesis of the product 10 via an a,b-unsaturated addition reaction of acetone cyanohydrin with compound 8, which afforded the product in 75% yield and 88:12dr. Moreover, Erikas et al. reported the synthesis of compound 13 via Michael conjugate addition of diethylaluminum cyanide to α,β-unsaturated substrate 11 (Scheme 2), in which the synthesized derivative showed moderate enantioselectivity[7].
References
- Calandre, E. P.; Rico-Villademoros, F.; Slim, M. Alpha2delta Ligands, Gabapentin, Pregabalin and Mirogabalin: A Review of Their Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutic Use. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 1263–1277.
- Bassas, O.; Huuskonen, J.; Rissanen, K.; Koskinen, A. M. P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 9, 1340–1351. DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.200801220.
- McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2248
- Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2539
- McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2248
- Derry S, Bell RF, Straube S, Wiffen PJ, Aldington D, Moore RA. Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 23;1(1):CD007076. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007076.pub3. PMID: 30673120; PMCID: PMC6353204.
- Chasheng He, Ziran Zhai, Yang Zhou, Jianqi Li & Guan Wang (2021) A new synthetic route for the preparation of pregabalin, Synthetic Communications, 51:13, 2034-2040, DOI: 10.1080/00397911.2021.1919710
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Pregabalin manufacturers

US $10.00/ASSAYS2024-05-05
- CAS:
- 148553-50-8
- Min. Order:
- 1ASSAYS
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10 tons

US $0.00/G2024-05-02
- CAS:
- 148553-50-8
- Min. Order:
- 1G
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20


