What is 2,5-Hexanedione?Uses,Synthesis,Detection method
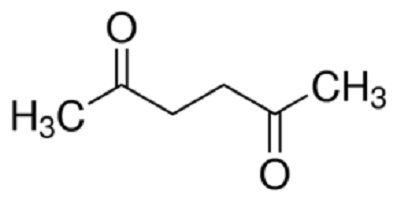
2,5-Hexanedione (Acetonylacetone) is an aliphatic diketone. It is a Clear colorless to amber liquid with a sweet aromatic odor. In humans, it is a toxic metabolite of hexane and of 2-hexanone.
Uses
Acetonylacetone can be used in the synthesis of isocarboxazid,rolgamidine,and mopidralazine. Treatment with P4S10 gives 2,5-dimethylthiophene.
Synthesis
2,5-Hexanedione has been prepared in several ways. A common method involves hydrolysis of 2,5-dimethylfuran, a glucose derived heterocycle.
Purification Methods
Purify it by dissolving in Et2O, stiring with K2CO3 (a quarter of the weight of dione), filtering, drying over anhydrous Na2SO4 (not CaCl2), filtering again, evaporating the filtrate and distilling it in a vacuum. It is then redistilled through a 30cm Vigreux column (p 11, oil bath temperature 150o). It is miscible with H2O and EtOH. The dioxime has m 137o (plates from *C6H6), the mono-oxime has b 130o/11mm, and the 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone has m 210-212o (red needles from EtOH). It forms complexes with many metals.
Mechanism of Toxicity
Identification of 2,5-hexanedione as the major neurotoxic metabolite of n-hexane proceeded rapidly after its discovery as a urinary metabolite. 2,5-Hexanedione has been found to produce a polyneuropathy indistinguishable from n-hexane. 2,5-Hexanedione is many times more potent than n-hexane, the parent compound, in causing neurotoxicity in experimental animals. It appears that the neurotoxicity of 2,5-hexanedione resides in its γ-diketone structure since 2,3-, 2,4-hexanedione and 2,6-heptanedione are not neurotoxic, while 2,5-heptanedione and 3,6-octanedione and other γ-diketones are neurotoxic.
Detection method
2,5-Hexanedione is a main metabolite of n-hexane and is considered as the cause of n-hexane polyneuropathy. Therefore, it is useful to measure 2,5-hexanedione for biological monitoring of exposure to n-hexane. The analytical methods existing for n-hexane metabolites, however, were controversial and not established enough.
Hence, a simple and precise method for determination of urinary 2,5-hexanedione has been developed. Five ml of urine was acidified to pH 0.5 with concentrated hydrochloric acid and heated for 30 minutes at 90-100 degrees C. After cooling in water, sodium chloride and dichloromethane containing internal standard were added. The sample was shaken and centrifuged. 2,5-Hexanedione concentration in an aliquot of dichloromethane extract was quantified by gas chromatography using a widebore column (DB-1701). Urinary concentration of 2,5-hexanedione showed a good correlation with exposure to n-hexane (n = 50, r = 0.973, p less than 0.001). This method is simple and precise for analysis of urinary 2,5-hexanedione as an index of exposure to n-hexane.
);You may like
Lastest Price from 2,5-Hexanedione manufacturers

US $5.00-2.00/KG2023-06-17
- CAS:
- 110-13-4
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10000kg
US $100.00/KG2023-01-10
- CAS:
- 110-13-4
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%min
- Supply Ability:
- 200TON

