What is the ionic charge of silicon?
Silicon typically forms ions with a charge of +4. This means it can lose four electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases. When silicon loses these electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion, often referred to as a cation. The resulting silicon cation has a 4+ charge.
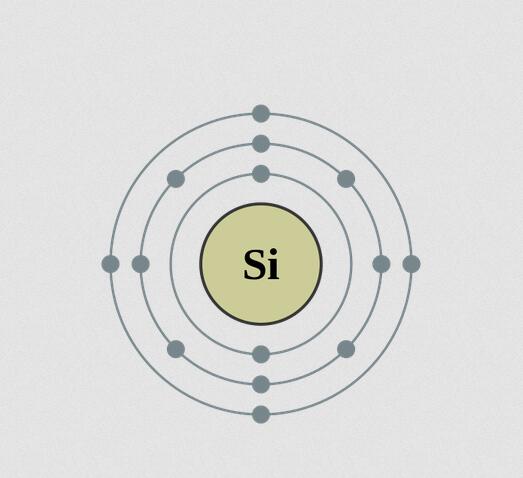
Silicon (Si), a nonmetallic chemical element in the carbon family (Group 14 [IVa] of the periodic table). Silicon makes up 27.7 percent of Earth’s crust; it is the second most abundant element in the crust, being surpassed only by oxygen.
The name silicon derives from the Latin silex or silicis, meaning “flint” or “hard stone.” Amorphous elemental silicon was first isolated and described as an element in 1824 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius, a Swedish chemist. Impure silicon had already been obtained in 1811. Crystalline elemental silicon was not prepared until 1854, when it was obtained as a product of electrolysis. In the form of rock crystal, however, silicon was familiar to the predynastic Egyptians, who used it for beads and small vases; to the early Chinese; and probably to many others of the ancients. The manufacture of glass containing silica was carried out both by the Egyptians—at least as early as 1500 bce—and by the Phoenicians. Certainly, many of the naturally occurring compounds called silicates were used in various kinds of mortar for construction of dwellings by the earliest people.
On a weight basis, the abundance of silicon in the crust of Earth is exceeded only by oxygen. Estimates of the cosmic abundance of other elements often are cited in terms of the number of their atoms per 106 atoms of silicon. Only hydrogen, helium, oxygen, neon, nitrogen, and carbon exceed silicon in cosmic abundance. Silicon is believed to be a cosmic product of alpha-particle absorption, at a temperature of about 109 K, by the nuclei of carbon-12, oxygen-16, and neon-20. The energy binding the particles that form the nucleus of silicon is about 8.4 million electron volts (MeV) per nucleon (proton or neutron). Compared with the maximum of about 8.7 million electron volts for the nucleus of iron, almost twice as massive as that of silicon, this figure indicates the relative stability of the silicon nucleus.
);You may like
Lastest Price from Silicon manufacturers

US $15.00-10.00/KG2021-07-02
- CAS:
- 7440-21-3
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability:
- Monthly supply of 1 ton

US $1.00/kg2019-07-06
- CAS:
- 7440-21-3
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- Customized


![1209012-31-6 4,9-dihydro-s-indaceno[1,2-b:5,6-b’]dithiophenePolymersElectrochromic devices](/NewsImg/2024-02-07/6384290979396803394107656.png)