2-Thiobarbituric Acid: Overview and Applications as a Corrosion Inhibitor
General Description
2-Thiobarbituric acid is a versatile organic compound with a unique structure that offers both acidic and reactive properties, making it highly beneficial in biochemistry for detecting lipid peroxidation and as a building block in synthetic chemistry. Its thiol group's reactivity allows for the creation of compounds with specific properties. Additionally, 2-Thiobarbituric acid has proven to be an effective, eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for API 5L X60 steel in oilfield environments, demonstrating over 90% efficiency under various conditions. 2-Thiobarbituric acid's action as a mixed-type inhibitor and the formation of a protective film through chemical adsorption highlight its potential in preventing corrosive damage, thus offering a sustainable solution for protecting oil and gas industry infrastructure.

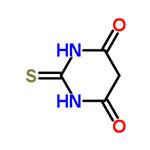
Figure 1. 2-Thiobarbituric acid
Overview
2-Thiobarbituric acid is a multifaceted organic compound characterized by its distinctive structure, which merges a barbituric acid core with a thiol group. This combination affords 2-Thiobarbituric acid unique acidic and reactive qualities, particularly due to the nucleophilic nature of its thiol group. This attribute renders it highly reactive towards electrophiles, paving the way for its application across diverse chemical and biological landscapes. One of the hallmark uses of 2-Thiobarbituric acid is in the biochemistry realm, where it serves as a critical reagent in the detection of lipid peroxidation. This process, indicative of oxidative stress, involves the oxidation of lipids leading to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The interaction between peroxidized lipids and 2-Thiobarbituric acid results in the formation of a pink-colored complex known as thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS). The quantification of TBARS through spectrophotometry is a widely adopted method for assessing oxidative damage in biological systems. Beyond its biochemical significance, 2-Thiobarbituric acid's reactive thiol group makes it an invaluable asset in synthetic chemistry. It acts as a versatile building block for the generation of various derivatives through facile substitution reactions. This capability enables the synthesis of compounds with customized properties, expanding 2-Thiobarbituric acid's utility across different scientific domains. In essence, 2-Thiobarbituric acid stands out as a pivotal compound with broad-ranging applications, from serving as a biomarker for oxidative stress to facilitating the synthesis of novel chemical entities. Its unique structural features and reactive potential underscore its importance in advancing research and development in science. 1
Applications as a corrosion inhibitor
2-Thiobarbituric acid has been identified as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for API 5L X60 steel in environments that simulate conditions found in sweet oilfields. This application is crucial because it addresses the need for sustainable methods to protect infrastructure in the oil and gas industry from corrosive damage, particularly in settings where carbon dioxide and chloride ions are prevalent. The study exploring 2-Thiobarbituric acid's effectiveness utilized several sophisticated techniques, including linear polarization resistance (LPR), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and potentiodynamic polarization (PDP), alongside surface analysis methods like scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The research findings demonstrated that 2-Thiobarbituric acid could achieve corrosion inhibition efficiencies greater than 90% under a variety of conditions, including different concentrations of 2-Thiobarbituric acid (ranging from 25 to 100 ppm), solution pH levels (4 and 6), temperature ranges (25 to 80°C), and immersion times (2 to 72 hours). Such high efficiency across diverse conditions highlights 2-Thiobarbituric acid's robustness as a corrosion inhibitor. Notably, 2-Thiobarbituric acid was found to act as a mixed-type inhibitor according to PDP results, suggesting it can mitigate both anodic and cathodic reactions involved in the corrosion process. The mechanism behind 2-Thiobarbituric acid's protective action involves its chemical adsorption onto the steel surface, adhering to the Langmuir isotherm model. This indicates a strong and specific interaction between 2-Thiobarbituric acid molecules and the metal surface, forming a protective film that significantly reduces corrosion rates. The composition and structure of this adsorbed film were further analyzed using XPS, providing insights into the molecular interactions at play. Overall, 2-Thiobarbituric acid's application as a corrosion inhibitor for steel in oilfield environments showcases its potential as a sustainable solution for corrosion protection in critical industrial applications. 2
Reference
1. 2-Thiobarbituric acid. National Center for Biotechnology Information (2024). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 2723628.
2. Usman BJ, Gasem ZM, Umoren SA, Solomon MM. Eco-friendly 2-Thiobarbituric acid as a corrosion inhibitor for API 5L X60 steel in simulated sweet oilfield environment: Electrochemical and surface analysis studies. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):830.
);You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from 2-Thiobarbituric acid manufacturers

US $1.10/g2024-04-17
- CAS:
- 504-17-6
- Min. Order:
- 1g
- Purity:
- 99.0% min
- Supply Ability:
- 100 tons min
US $10.00-0.80/KG2024-03-25
- CAS:
- 504-17-6
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- g-kg-tons, free sample is available