The applications of carbon tetrabromidein organic synthesis
Introduction
carbon tetrabromide (CBr4) is the simplest (tetrahedral) building element. Indeed, this prototypical electron acceptor forms intermolecular complexes with one-dimensional donors, the charge-transfer nature of which has been revealed in a series of physical-chemical studies. Although the isolation of crystalline solids met significant difficulties due to the relatively low free energy of the complex formation, we earlier found stronger charge-transfer complexes of CBr4 using better electron donors, especially tertiary aliphatic amines. On the basis of that study, Desiraju and co-workers attempted an assembly of crystalline diamondoid donor/acceptor networks using hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) as the tetrahedral donor core.The resulting diamondoid (sphaleroid) network suffered from positional disorder between CBr4 and HMT (because of their similar size). A subsequent attempt to stabilize an extended tetrabromoadamantane/HMT network, using an excess of tetrahedral CBr4 to fill the cavities, resulted in a much weaker (and also disordered) donor/acceptor assembly.13b Additionally, these systems lacked continuous electronic coupling (i.e., through-orbital interaction) within their diamondoid networks because of the nonconducting nature of aliphatic CH2-bridges in the HMT and (tetrabromo)adamantane units[1]
An efficient and useful catalyst—carbon tetrabromide (CBr4)—was discovered to be highly effective for the acylation of phenols, alcohols, and thiols under metal- and solvent-free conditions.
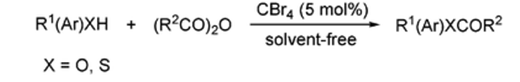
Picture 1 An efficient and useful catalyst—carbon tetrabromide
Although carbon tetrabromide is considered a poisonous, irritating solid (skin contact can cause severe irritation; avoid inhalation of fumes; toxicity: irritating to skin, eyes and respiratory[1].
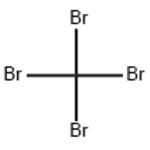
Structure
At atmospheric pressure, CBr 4 undergoes a transition at 47°C; phase I is stable between 92°C (melting point) and 47°C, phase II below 47°C. Finbak & Hassel (1937) have shown that phase II is monoclinic with a = 21.12, b = 12.26, c = 24.14 A, fl = 125 ° 3', Z = 32. These results disagree with those of Mark (1924). Harris (1962) gives a~ = 20.9, a~ = 21.2, a~ = 12. I A, fl = 110 ° 30'. He suggests that the space group is C2/c but did not determine the structure. Phase I is face-centred cubic with Z = 4 (Wyckoff, 1964), and is characterized by molecular reorientations ('plastic' crystal). It is interesting to consider why and how the transition occurs[2].
The asymmetric unit contains four molecules. Each C atom is assumed to lie at the centre of mass of its four Br atoms and to move isotropicallv.
Applications in organic synthesis
Carbon tetrabromide, as a commercially available and cheap reagent, has found many applications in organic synthesis, for example, the bromination reaction of benzene hydrocarbons, terminal acetylenes, alkanes, or arylalkanes, and active methylenes. The known Appel and Corey-Fuchs reactions represent another typical application of CBr4 in organic synthesis, which involve the initial formation of triphenylphosphine bromide (TPPB) or analogue via a SN2 type attacking of the phosphorus atom of PPh3 at a bromine atom of CBr4. The initial studies were focused on the investigation of the C-S cross[1]coupling of a dithiocarbamate, which was derived from the reaction of an amine and carbon disulfide, with an active methylene compound in the presence of CBr4. The design was based on the consideration that the C-S coupling might occur through a transient (dialkylamino(thiocarbonyl))- sulfenyl bromide intermediate which, similar to Appel agents, could be formed in situ by the nucleophilic attack of a dithiocarbamate anion on a bromine atom of CBr4, and then trapped by an active methylene compound to form an organic dithiocarbamate. C-S cross-coupling of an active methylene compound with a thiolate, a dithiocarbamate, a xanthate, or a benzodithioate can be achieved in the presence of carbon tetrabromide[3].
Carbon tetrabromide spontaneously forms a series of inter[1]molecular complexes with electron-rich halide anions (chloride, bromide, and iodide) that are characterized by the unusual strength and directionality as well as large electronic (HOMO[1]LUMO) couplings of the halide donor and CBr4 acceptor. Spectral (UV-vis) studies in solution establish the charge[1]transfer nature of the (CBr4/halide) interactions, and these combined with the tetrahedral shape of the acceptor lead to supramolecular (crystalline) assemblies of advanced 3-D (diamondoid) networks that are uniquely stabilized by the proper choice of tetraalkylammonium counterions to fill the adamantanoid cavities. Most importantly, the alternate population of the diamondoid nodes, consisting of contiguous donor (halide) and acceptor (CBr4) units, effectively results in the annihilation of inversion centers of symmetry, in agreement with the sphaleroid structural subclass.
Reference
1 More M, Baert F, Lefebvre J. Solid-state phase transition in carbon tetrabromide CBr4. I. The crystal structure of phase II at room temperature[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1977, 33(12): 3681-3684.
2 Zhang L, Luo Y, Fan R, et al. Metal-and solvent-free conditions for the acylation reaction catalyzed by carbon tetrabromide (CBr4)[J]. Green Chemistry, 2007, 9(9): 1022-1025.
3 Lindeman S V, Hecht J, Kochi J K. The charge-transfer motif in crystal engineering. Self-assembly of acentric (diamondoid) networks from halide salts and carbon tetrabromide as electron-donor/acceptor synthons[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(38): 11597-11606.
);You may like
Lastest Price from Carbon tetrabromide manufacturers
US $50.00-1.00/KG2024-03-25
- CAS:
- 558-13-4
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- g-kg-tons, free sample is available

US $0.00/KG2023-09-11
- CAS:
- 558-13-4
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 500000kg


