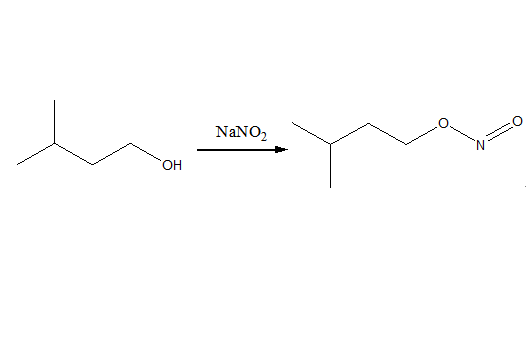
Uses of Amyl nitrite
Amyl nitrite had been used clinically as early as 1867, when the Scottish physician Sir Thomas Brunton used it as a vasodilator as treatment for angina pectoris in his patients. In the late 1880s, a protective effect on cyanide toxicity in canines was noted when amyl nitrite was inhaled postexposure. Amyl nitrite has been used clinically in a multicomponent cyanide antidote kit and is also a recreational drug of abuse.

Properties
Amyl nitrite is slightly soluble in water and is commonly supplied in ampoules that are broken and administered by inhalation. Inhalation is likely the most common route of exposure, though reports of ingestion of the liquid itself have been seen. Amyl nitrite may also be absorbed through the skin when skin comes in contact with the liquid.Amyl nitrite is an unstable compound. It is air and light sensitive and flammable. Amyl nitrite forms explosive mixtures with air or oxygen, and it is incompatible with oxidizing agents and reducing agents.
Uses
Amyl nitrite is employed medically to treat heart diseases as well as angina.
Amyl nitrite is sometimes used as an antidote for cyanide poisoning.It can act as an oxidant, to induce the formation of methemoglobin. Methemoglobin in turn can sequester cyanide as cyanomethemoglobin.
Amyl nitrite is used as a cleaning agent and solvent in industrial and household applications. It replaced dichlorodifluoromethane, an industrial chemical universally banned in 1996 due to damage to the ozone layer,as a printed circuit board cleaner.Trace amounts are added to some perfumes.
It is also used recreationally as an inhalant drug that induces a brief euphoric state, and when combined with other intoxicant stimulant drugs such as cocaine or MDMA, the euphoric state intensifies and is prolonged. Once some stimulative drugs wear off, a common side effect is a period of depression or anxiety, colloquially called a "come down"; amyl nitrite is sometimes used to combat these negative after-effects. This effect, combined with its dissociative effects, has led to its use as a recreational drug.
Mechanism of toxicity
The primary mechanism of toxicity develops from the powerful oxidative effects of nitrites on hemoglobin. Methemoglobinemia, which develops when the iron atom in hemoglobin loses one electron to an oxidant, causing a change from the ferrous (2+) state to the ferric (3+) state, may cause cellular hypoxia. When methemoglobin levels exceed 10–15%, cyanosis may be evident. Nitrites also cause vasodilation by direct action on smooth muscle. Physical effects include decreases in blood pressure, headache, flushing of the face, increased heart rate, dizziness, and relaxation of involuntary muscles, especially of the blood vessels and the anal sphincter.
Amyl nitrite may be irritating to the lungs and throat when breathed in. With exposure to the skin, amyl nitrite has irritant properties. It can also be readily absorbed, causing systemic effects with skin contact.
);You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Isoamyl nitrite manufacturers

US $0.00/Kg/Bag2023-06-29
- CAS:
- 110-46-3
- Min. Order:
- 1Kg/Bag
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20ton

US $200.00/kg2023-06-26
- CAS:
- 110-46-3
- Min. Order:
- 10kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 500kg/month