Folic acid (folate,59-30-3) is a kind of B-vitamin which is mainly present in the liver and kidney. It has various kinds of pharmacological and physiological effects. It is involved in amino acid metabolism, purine and pyrimidine synthesis, and is also essential for hematopoiesis and red blood cell generation. In women pregnancy, folate can effectively prevent neural tube defects in the baby. It plays important role in fertility through contributing to spermatogenesis. It can also reduce the incidence of heart disease, stroke and cancer.
Folate deficiency may lead to various kinds of diseases including glossitis, diarrhea, depression, confusion, anemia, and fetal neural tube defectsand brain defects (during pregnancy). Other symptoms may include fatigue, gray hair, mouth sores, poor growth, and swollen tongue.
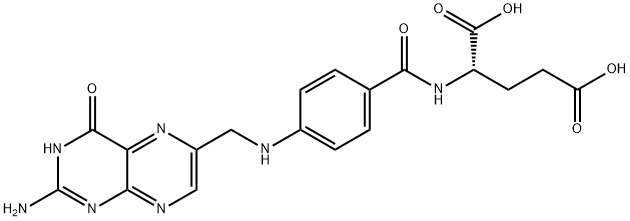
Folic acid is an essential B vitamin. It is converted to folate in vivo, which is a necessary cofactor for a variety of biological processes, including nucleotide synthesis and, thus, DNA synthesis and repair, among others. A deficiency in dietary folic acid can lead to a range of developmental and cognitive disorders, most prominently neural tube defects and congenital heart defects.
In the 1930s, brewer’s yeast was found to prevent anemia. Folic
acid was later discovered to be the nutrient responsible for this
effect and was purified in 1941 by Mitchell and coworkers
(Mitchell et al., 1941). Folate is needed for biosynthesis of
purines and thymidine for DNA and RNA synthesis in all cells.
It is also involved in metabolism of some of the amino acids
needed for protein synthesis, especially the conversions of
serine to glycine and homocysteine to methionine. This makes
the nutrient especially important during periods of rapid cell
division, such as in pregnancy. Folate is also involved in
transfer of one-carbon groups for methylation reactions. The
role of folate in cell division was capitalized upon in the
synthesis of aminopterin, a folate antagonist, which was one of
the first anticancer drugs produced.
orange to yellow crystalline powder
The folates include a large number of chemically related species, each differing
with respect to the various substituents possible at three sites on the pteroylglutamic
acid basic structure. More than 170 different folates are theoretically possible. Not
all of these occur in nature; but it has been estimated that as many as 100 different
forms are found in animals. The folates from most natural sources usually have a
single carbon unit at N-5 and/or N-10; these forms participate in the metabolism of
the single-carbon pool.
Folic acid (pteroylmonoglutamic acid) is an orange-yellow crystalline substance
that is soluble in water but insoluble in ethanol or less polar organic solvents. It is
unstable to light, to acidic or alkaline conditions, to reducing agents, and, except in
dry form, to heat. It is reduced in vivo enzymatically (or in vitro with a reductant
such as dithionite) first to 7,8-dihydrofolic acid (FH2) and then to FH4; both of these
compounds are unstable in aerobic environments and must be protected by the pres ence of an antioxidant (e.g., ascorbic acid, 2-mer
Two derivatives of folic acid, each having an amino group in the place of the
hydroxyl at C-4, are folate antagonists of biomedical use: aminopterin (4-aminofolic
acid) and methotrexate (4-amino-N10-methylfolic acid). Aminopterin is used as a
rodenticide; methotrexate is an antineoplastic agent.
Folvite, Lederle, US ,1946
folic acid is generally used as an emollient. In vitro and in vivo skin studies now indicate its capacity to aid in DnA synthesis and repair, promote cellular turnover, reduce wrinkles, and promote skin firmness. There is some indication that folic acid may also protect DnA from uV-induced damage. Folic acid is a member of the vitamin B complex and is naturally occurring in leafy greens.
A vitamin needed to synthesize DNA, conduct DNA repair and methylate DNA, it also acts as a cofactor in biological reactions involving folate.
Folic Acid is a water-soluble b-complex vitamin that aids in the for-
mation of red blood cells, prevents certain anemias, and is essential
in normal metabolism. high-temperature processing affects its sta-
bility. it is best stored at lower than room temperatures. it is also
termed folacin. it is found in liver, nuts, and green vegetables.
Literature tends to indicate that B vitamins cannot pass through the layers of the skin and, therefore, are of no value in the skin surface. Current experiments demonstrate, however, that vitamin B2 acts as a chemical reaction accelerator, enhancing the performance of tyrosine derivatives in suntan-accelerating preparations.
ChEBI: An N-acyl-amino acid that is a form of the water-soluble vitamin B9. Its biologically active forms (tetrahydrofolate and others) are essential for nucleotide biosynthesis and homocysteine remethylation.
The following description is taken from US Patent 2,956,057.
100 grams of 1,3,3-trichloroacetone are heated on a boiling water bath and
95 grams of bromine are added thereto in drops while being stirred and the
stirring is continued for about 1 hour. The resulting reaction solution is
distilled under reduced pressure. 115 grams of 1-bromo-1,3,3-
trichloroacetone are obtained having a boiling point of 85° to 95°C/17 mm
(Hg).
For the preparation of the hydrate, 100 grams of water are added to 100
grams of 1bromo-1,3,3-trichloroacetone, which is agitated and cooled. A white
scaly crystal of hydrate of 1-bromo-1,3,3-trichloroacetone is obtained (100
grams), having a melting point of 52° to 53°C.
8.9 grams of 2,4,5-triamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine hydrochloride and 8 grams
of p-aminobenzoylglutamic acid are dissolved in 400 cc warm water, which is
cooled at 35° to 27°C and adjusted to pH 4 by using 20% caustic soda
solution. To this solution was simultaneously added dropwise a solution
obtained by dissolving 13.4 grams of 1-bromo-1,3,3-trichloroacetone hydrate
in 90 cc of 50% methanol and 24 grams of 35% aqueous sodium bisulfite
solution over a period of approximately 2 hours. During this period, in order
to maintain the pH value of the reaction solution at 4 to 5, 20% caustic soda
solution is added from time to time. The precipitate, formed by stirring for 5
hours after dropping was finished, is filtered, and the filtrated precipitate is
refined; 5.6 grams of pure pteroylglutamic acid is obtained.
Treatment of B vitamin (folacin) deficiency
Odorless orange-yellow needles or platelets. Darkens and chars from approximately 482°F.
Insoluble in water. Aqueous solutions have pHs of 4.0-4.8.
Acid solutions of Folic acid are sensitive to heat, but towards neutrality, stability progressively increases. Solutions are inactivated by ultraviolet light and alkaline solutions are sensitive to oxidation. Folic acid is also inactivated by light. Folic acid is incompatible with oxidizing agents, reducing agents and heavy metal ions.
Flash point data for Folic acid are not available; however, Folic acid is probably combustible.
A nutritional delivery form of folate. Folic acid and its derivatives are essential mediators of one-carbon metabolism within cells.
Folate-deficient megaloblastic anaemia
Supplement in HD patients
Poison by
intraperitoneal and intravenous routes.
Experimental teratogenic effects. Mutation
data reported. When heated to
decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Folic acid is used to treat folic acid deficiency in dogs, cats, and
horses (theoretically in other animal species as well) often due to
small intestinal disease. Cats with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
appear to be most at risk for folate and cobalamin deficiencies secondary
to malabsorption of folic acid in the diet. Dogs with exocrine
pancreatic insufficiency often are noted to have increased folate levels
secondary to overgrowths of folate-synthesizing bacteria in the
proximal small intestine. Chronic administration of dihydrofolate
reductase inhibiting drugs such as pyrimethamine, ormetoprim or
trimethoprim can potentially lead to reduced activated folic acid
(tetrahydrofolic acid); folic acid supplementation is sometimes prescribed
in an attempt to alleviate this situation.
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antiepileptics: reduces phenytoin, primidone and
phenobarbital levels.
Cytotoxics: avoid with raltitrexed.
Folic acid given therapeutically enters the portal
circulation largely unchanged, since it is a poor substrate
for reduction by dihydrofolate reductase. It is converted
to the metabolically active form 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
in the plasma and liver. Folate undergoes enterohepatic
circulation. Folate metabolites are eliminated in the urine
and folate in excess of body requirements is excreted
unchanged in the urine.
If paper chromatography indicates impurities, then recrystallise it from hot H2O or from dilute acid [Walker et al. J Am Chem Soc 70 19 1948]. Impurities may be removed by repeated extraction with n-BuOH of a neutral aqueous solution of folic acid (by suspending in H2O and adding N NaOH dropwise till the solid dissolves, then adjusting the pH to ~7.0-7.5) followed by precipitation with acid, filtration, or better collected by centrifugation and recrystallised form hot H2O. [Blakley Biochem J 65 331 1975, Kalifa et al. Helv Chim Acta 6 1 2739 1978.] Chromatography on cellulose followed by filtration through charcoal has also been used to obtain pure acid. [Sakami & Knowles Science 129 274 1959.] UV: max 247 and 296nm ( 12,800 and 18,700) in H2O pH 1.0; 282 and 346nm ( 27.600 and 7,200) in H2O pH 7.0; 256, 284 and 366nm ( 24600, 24,500 and 86,00) in H2O pH 13 [Rabinowitz in The Enzymes (Boyer et al. Eds), 2 185 1960]. [Beilstein 26 III/IV 3944.]